On April 19, 2023, in line with the EU’s strengthened climate goals and the Strategic Framework for Sustainable and Smart Mobility, the European Parliament and the Council agreed to strengthen CO2 emissions performance standards for new passenger cars and new light commercial vehicles in line with the Paris Agreement.
The legislation will be implemented in two phases:
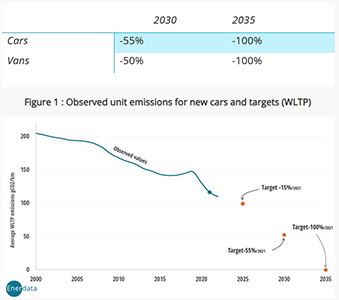
1. Intermediate phase: 15% reduction by 2025 for cars, 55% by 2030 for cars, and 50% by 2030 for trucks (compared to 2021).
2. Final target: 100% reduction in average emissions for cars and trucks by 2035.
The legislation sets an average emission level of 95 gCO2/km for the new fleet in 2020. The latter target is expressed based on the old NEDC standard2. Figure 1 shows the evolution of European emissions targets based on the latest WLTP standard.
The market is driven by the growing demand for cleaner and smarter cars across Europe, stringent emission regulations imposed by governments, and rising awareness about the adverse effects of these emissions on climate change. In addition, improving economic conditions among people have also increased the demand for electric vehicles (EVs), especially passenger cars. The European electric private car market is expected to grow at a CAGR of about 18% during the forecast period 2022-27.
In addition to regulatory standards, the EV market is also dependent on the infrastructure of charging stations. Countries such as Germany, France, and the UK have mandated the installation of EV charging stations in new buildings. Moreover, the EU will require the installation of 400-600 kW charging stations every 60 km. These regulations are key steps towards a more sustainable future.

Save cost-with manufacturer direct pricing
Control quality-with strict quality control and testing
Save time-with experienced team to get project done